Summary
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) is a hard fork of the Go Ethereum (Geth) protocol and has many similarities with the Ethereum blockchain. However, the developers of BSC have made significant adjustments to some key points. The biggest change is reflected in BSC’s consensus mechanism, which ultimately successfully reduced transaction fees and increased transaction speed.
Introduction
At first glance, Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and Ethereum are very similar. DApps and tokens built in BSC are compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). You may have noticed that your public wallet address is exactly the same in both blockchains, and there are even cross-chain projects running in both networks. Still, there are significant differences between the two blockchains. Before deciding which blockchain to use, it’s best to first understand the differences between the two.
Blockchain Traffic and DApp Ecosystem
As of 2021 In June, Ethereum hosted more than 2,800 DApps on the blockchain, while BSC had about 810. Although the gap is huge, considering that BSC is in the ascendant, this powerful and continuously developing ecosystem is worth looking forward to.
Active addresses are also important on-chain indicators to consider. Although it is an emerging blockchain, BSC set a record of 2,105,367 addresses on June 7, 2021, more than twice the all-time high of Ethereum on May 9, 2021 (799,580 addresses).
What is the reason for the sudden surge of BSC? Mainly thanks to shorter confirmation times and lower fees. BSC’s growth may also be related to the hype surrounding non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and compatibility with popular cryptocurrency wallets such as Trust Wallet and MetaMask.
If you compare the daily transaction data, the difference between the two is even more obvious. Through BSC, users can transfer funds and interact with smart contracts more quickly and cost-effectively. As shown in the figure below, BSC’s daily trading volume peaks at approximately 12 million, and currently exceeds 4 million.
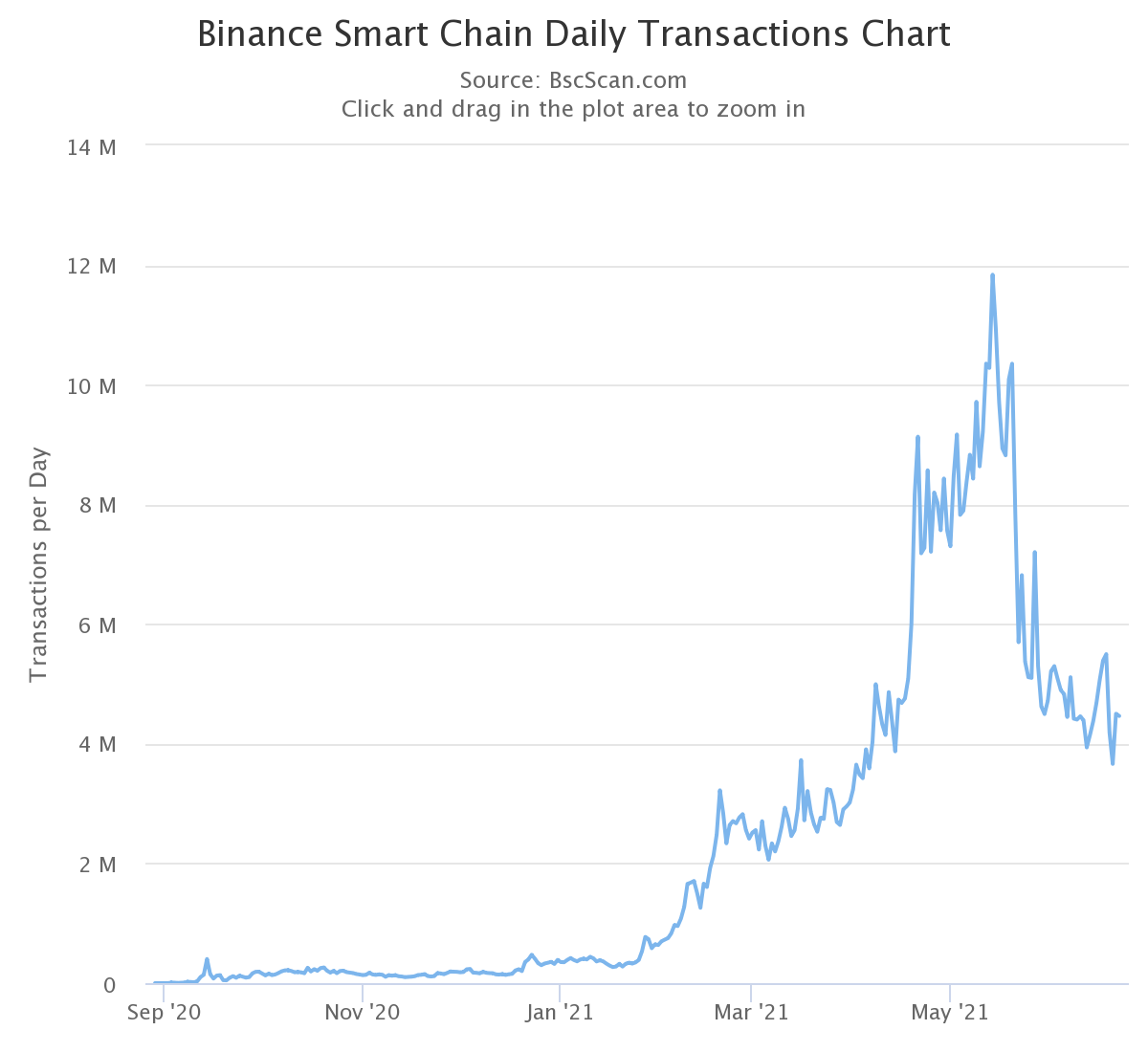
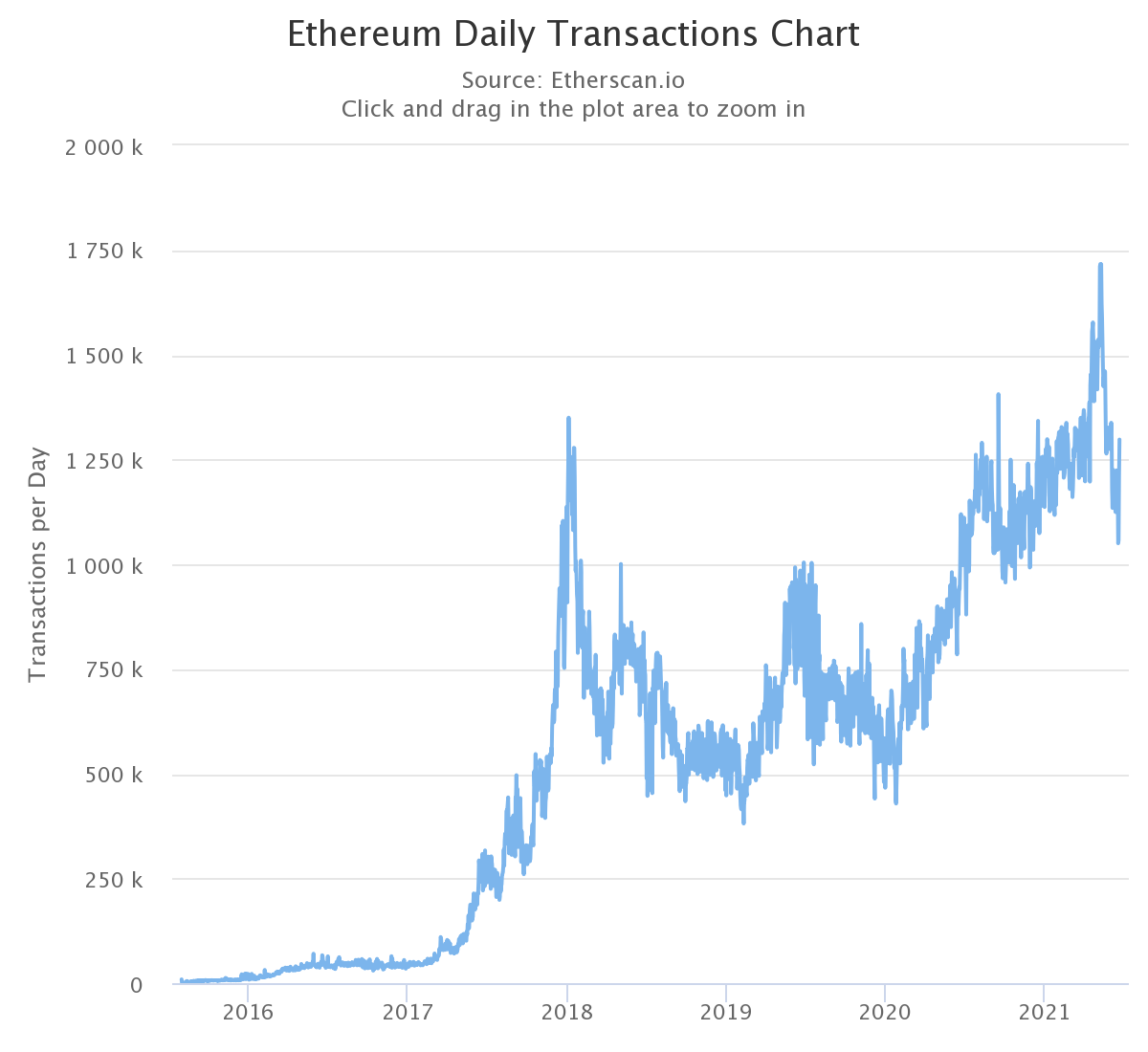
In contrast, Ethereum’s daily transaction volume has never exceeded 1.75 million. For users who need to transfer funds regularly, BSC seems to be more popular. Of course, daily transaction volume analysis also needs to be judged in combination with active addresses. At the time of writing, BSC has more users and its average trading volume is higher.
The most commonly used DeFi DApp in Ethereum and BSC
In terms of decentralized finance, there are a large number of DApp cross-products between BSC and Ethereum due to blockchain compatibility. Developers can easily port applications from Ethereum to BSC, and new BSC projects often reuse open source code from Ethereum, simply renaming it. Let’s take a look at the top five Ethereum DApps ranked by DAppRadar users.
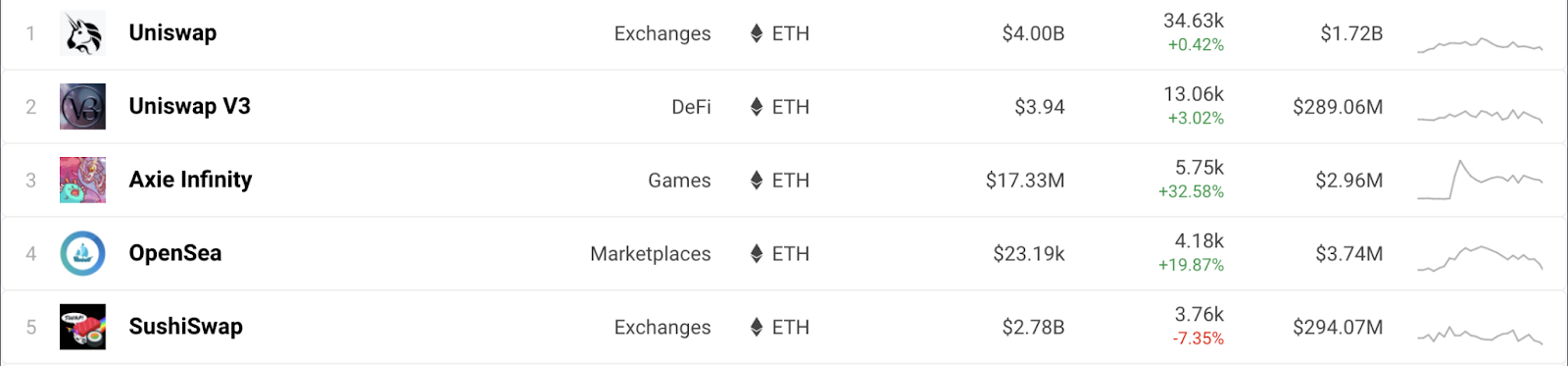
Before the list The five are diverse, including two DeFi automated market makers (Uniswap and SushiSwap), a cryptocurrency game (Axie Infinity), and a peer-to-peer marketplace (OpenSea). Compare BSC's top five and you'll find many similarities.

PancakeSwap was created as a hard fork of Uniswap. Both Autofarm and Pancake Bunny are liquidity mining farms, but Ethereum does not appear in the top five in this category. Both Biswap and Apeswap are automated market makers. Binance Smart Chain has low fees and significantly increases transaction speeds, so liquidity mining farms within it tend to be more efficient. Driven by these factors, liquidity mining has become a popular choice for BSC users.
When it comes to cryptocurrency games, many of the hottest games have indeed been born in Ethereum. Although BSC also has some projects that are very similar to "CryptoKitties" and Axie Infinity, they have not been able to capture a large number of players like Ethereum Classic.
Transfer between networks
If you have ever deposited any BEP-20 or ERC-20 token into your wallet, you may have noticed that the wallet addresses for Ethereum and BSC are exactly the same . For example, if you mistakenly select the target network when withdrawing coins on an exchange, they can be easily retrieved from other blockchains.
If you accidentally withdraw ERC-20 tokens to BSC, you can still retrieve them at the corresponding BSC address. Conversely, the same process can be followed in order to retrieve tokens transferred from BSC to Ethereum. Fortunately, in both cases, your funds are not permanently lost. For detailed guidance, read How to Retrieve Cryptocurrency on Binance that was Transferred to the Wrong Network.
Transaction fee
Both BSC and Ethereum charge transaction fees based on the gas fee model as a measure of transaction complexity. BSC users can set the gas price according to network needs, and miners will prioritize transactions with higher gas prices. However, Ethereum’s London hard fork implemented some new tweaks and users will likely say goodbye to high fees.
The Ethereum upgrade creates a new pricing mechanism with a base fee for each block. The basic fee changes with transaction needs, and users do not need to decide the gas price by themselves.
Historical data shows that Ethereum’s gas fee is much higher than BSC. The highest average price was $68.72, which occurred in May 2021. Today, this trend has changed, but the price of Ethereum is still higher than BSC.
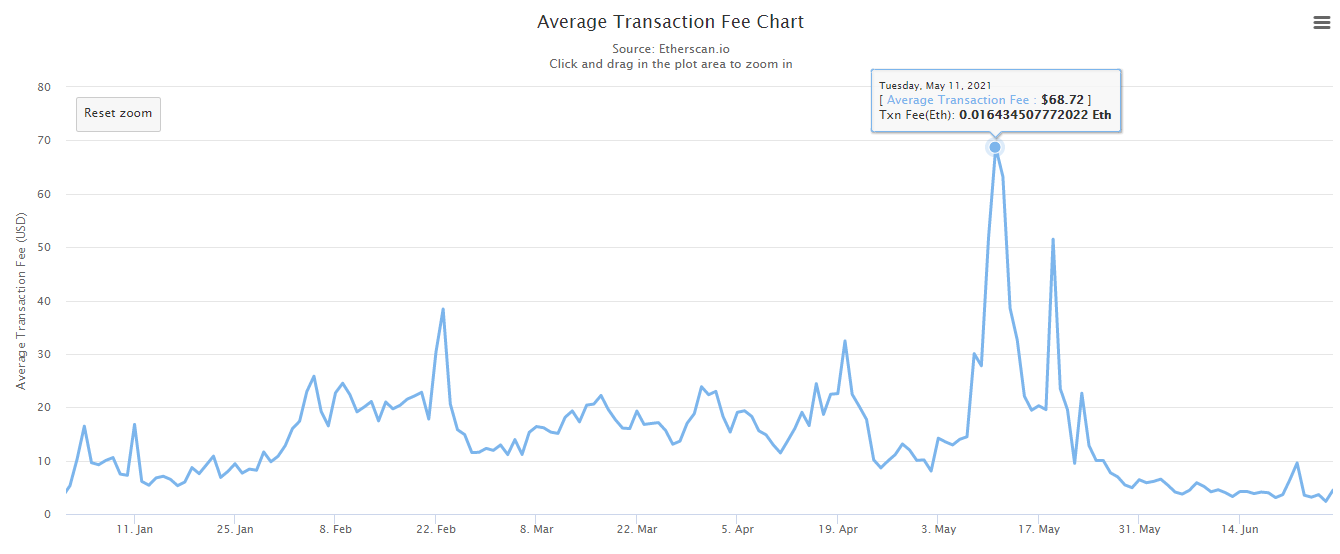
To understand more deeply, let’s take a look at the average Ethereum cost in Etherscan. The first three charts show Ethereum’s current gas price. For BSC and Ethereum, 1 Gwei corresponds to 0.000000001 Binance Coin or Ethereum respectively. The lower the price you pay, the longer it will take to complete the transaction.
If you just transfer ERC-20 tokens to another wallet, the average price you need to pay at the time of writing this article is 2.46 Dollar. When using the Uniswap liquidity pool involving multiple transactions, the price increased to $7.58.

The picture below is A transaction in BSC with a fee of just $0.03 is equivalent to an ERC-20 transfer on the Ethereum gas fee tracking page. BSC calculates this figure by multiplying the fuel used in the transaction (21,000) by the fuel fee price (5 Gwei).

Transaction Time
Measuring the average transaction in the blockchain Time is more complicated. From a technical perspective, as long as the miner verifies that the transaction is in the block, the transaction is completed, but other factors will still extend the waiting time:
If the fees are not set high enough, miners may delay your transaction or even not include it in any blocks at all.
More complex interactions with the blockchain require multiple transactions. For example, inject liquidity into liquidity pools.
Most services will only consider a transaction valid after a certain number of blocks have been confirmed. These additional confirmation operations reduce the risk for merchants and service providers to reverse chargebacks after a block is rejected by the network.
The Ethereum gas fee statistics above show that transaction times range from 30 seconds to 16 Minutes vary. These figures take into account successful transactions but do not take into account requirements regarding multiple confirmations.
For example, if you deposit Ether (ERC-20) into your Binance account, you will need to wait for 12 network confirmations. While it takes about 13 seconds to mine a block (as shown in the figure below), the time required to deposit Ether into the spot wallet will increase by an additional 156 seconds.

BSC’s average block generation time is 3 seconds. Compared with Ethereum’s 13 seconds, the speed is increased by about 4.3 times.

Consensus mechanism
Although Ethereum’s workload proof ( The PoW) consensus mechanism is similar to Bitcoin, but there are still significant differences from BSC's Authoritative Proof of Stake (PoSA). However, this difference doesn't last long. In Ethereum 2.0, the network will switch to a proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism.
BSC’s PoSA combines Proof of Authority (PoA) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). 21 validators take turns producing blocks and are rewarded with Binance Coin transaction fees in return. To become a validator, you need to run a node and stake at least 10,000 Binance Coins before you are eligible to become an elected candidate.
Other users are called principals, and elected candidates Later stake Binance Coin. The 21 elected candidates with the highest staked amounts will then take turns processing the blocks. The entire process repeats every 24 hours. Delegators can also share in the rewards earned by validators.
Ethereum’s PoW is a unique system that does not rely on the community but solves computing problems. Contest to select validators. Anyone can join, but participants must purchase or rent specialized mining equipment. The more computing power you have, the better your chances of being the first to solve the puzzle and verify the block. Successful miners will be rewarded with transaction fees and ether.
Although PoW is an effective way to create consensus and ensure network security, developers have never stopped exploring other mechanisms. They hope to find more efficient and environmentally friendly alternatives without compromising safety.
For the above reasons, the Ethereum network will eventually switch to proof of stake. Validators will stake Ether and gain the opportunity to produce blocks. Other validators will "validate" the block and check its correctness. If someone produces a block that contains fake transactions, they risk losing all of their staked tokens. Validators are then rewarded for successful blocks and verification work done. Malicious validators who directly deposit and stake large amounts of ether could lose their funds.

Summary
In summary, Binance Smart Chain There are obviously many similarities with Ethereum. To some extent, Ethereum users can easily migrate and experience BSC. While there are similarities, BSC implemented a number of meaningful adjustments in an effort to improve performance and efficiency. The Authoritative Proof of Stake (PoSA) consensus mechanism brings cheaper and faster blockchain transactions to users.


 Forum
Forum Finance
Finance
 Specials
Specials
 On-chain Eco
On-chain Eco
 Entry
Entry
 Podcasts
Podcasts
 Activities
Activities
 OPRR
OPRR
